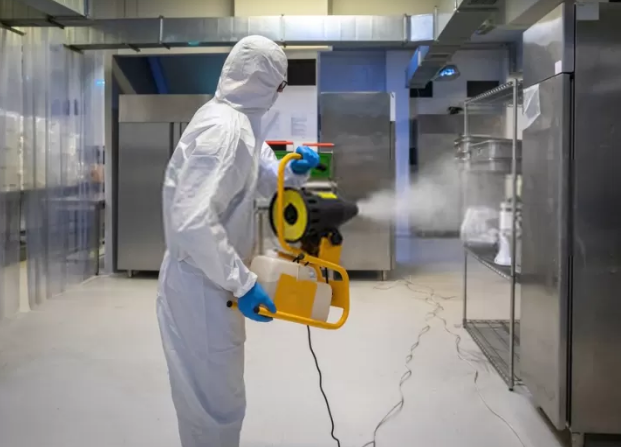
Chlorine dioxide uses include various purposes in different industries and settings. Chlorine dioxide is used for cleaning and sanitizing chemicals and application equipment in various industries, including food and beverage. Its versatility extends to applications such as pasteurization equipment, heat exchangers, cooling towers, hard surface disinfection, potable water treatment, and odor control in rendering plants.
Chlorine dioxide uses are favored above other sanitizers in the dairy, food and beverage, canning, and meat industries for controlling microbiological growth for which the FDA has approved the use of chlorine dioxide.
Chlorine dioxide is a gas with a yellowish-green color commonly employed for water disinfection. It’s remarkable anti-bacterial and anti-viral properties make it highly valuable in various applications. Composed of one chlorine and two oxygen atoms, chlorine dioxide finds extensive use in different fields.
Safe Drinking Water Treatment
Chlorine dioxide is predominantly utilized for disinfecting drinking water, surpassing the effectiveness of chlorine. In the realm of drinking water disinfection, it is widely employed worldwide. It efficiently eliminates Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium, which are major causes of water-borne diseases.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlights its addition to drinking water as a measure to safeguard individuals from harmful bacteria and microorganisms.
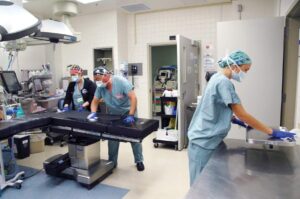
Medical Sanitization and Virucide
Chlorine dioxide gas finds application in medical environments, where it aids in sterilizing equipment, surfaces, rooms, surgical instruments, and tools. Additionally, chlorine dioxide acts as a reliable virucide, effectively combating disease-causing viruses like influenza and measles on non-porous hard surfaces, and it serves as a preventive measure against Legionnaires’ disease, caused by legionella bacteria.
Industrial Biocide
In the industrial sector, chlorine dioxide uses for controlling bacteria and mold and in biological sanitization among industries such as oil and gas, food and beverage production, and municipal applications. Chlorine dioxide biocides play a significant role in large-scale projects such as irrigation, cooling towers, and even swimming pools.
Food and Beverage Production
Chlorine dioxide acts as an antimicrobial agent in water utilized during poultry processing and the washing of fruits and vegetables. poultry, beef, seafood, microbrewery, fruit, and vegetable processing.
Paper Processing
Chlorine dioxide is instrumental in the chemical processing of wood pulp for paper manufacturing. It reduces the production of organochlorine compounds and exhibits 2.5 times more oxidizing power than chlorine. The ECF chlorine bleaching technique, utilizing chlorine dioxide, accounts for 95% of bleached pulp production.
Air Cleaning
Chlorine dioxide can enhance air quality due to its strong oxidation power. It is capable of combating airborne pathogens and eliminating bacteria that are resistant to other biocides, including hydrogen peroxide in certain cases. Chlorine dioxide proves to be an excellent solution for eliminating airborne mold particles.
Mouthwash
Chlorine dioxide has been proven effective in combating bad breath. When combined with water, it functions as a mouthwash. Its uses also include the treatment and prevention of gum disease and teeth whitening. However, it is important to note that routine dental care is still necessary.
Biofilm Dispersal
Biofilm, which can lead to issues such as corrosion and heat transfer restrictions, is effectively treated with chlorine dioxide.
FDA, CDC, USDA, and EPA Approved
Chlorine dioxide is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), it exhibits potency comparable to peracetic acid while being more cost-effective. Notably, it has a lesser impact on the environment compared to quaternary ammonium salts, chlorine, or bromine. These qualities make it an excellent choice for food processing plants, offering versatility, reduced harm, and the ability to destroy and prevent biofilms, a significant challenge in combating harmful bacteria. Unlike chlorine, it does not possess corrosive properties.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of chlorine dioxide uses, showcasing its significance and effectiveness in various industries and settings.








Leave a Reply